A four – axis rotary table is a crucial device in various manufacturing and machining processes. This blog will explore its working principle and real – world applications.
Working Principle
At its core, a four – axis rotary table consists of four axes of movement. These axes are typically labeled as X, Y, Z, and an additional rotational axis, often denoted as A.
X – Axis Movement
The X – axis is responsible for horizontal linear movement. It allows the workpiece or the tool (depending on the setup) to move back and forth along a straight line in the horizontal plane. For example, in milling operations, it can position the workpiece precisely under the cutting tool for different machining operations.
Y – Axis Movement
The Y – axis provides movement perpendicular to the X – axis in the horizontal plane. This axis, together with the X – axis, enables two – dimensional positioning of the object. In a CNC machining center, the combined movement of X and Y axes can create complex shapes on a flat surface of the workpiece.
Z – Axis Movement
The Z – axis is for vertical movement. It controls the up – and – down motion of either the workpiece or the tool. In drilling operations, the Z – axis moves the drill bit down to create holes in the workpiece at the desired depth.
Rotational Axis (A – Axis)
The A – axis is the rotational axis. It allows the workpiece to be rotated around a specific axis. This rotation is extremely useful when machining complex geometries. For instance, when creating angled surfaces or features on a cylindrical part, the A – axis can rotate the workpiece to the appropriate angle so that the cutting tool can shape it accurately.
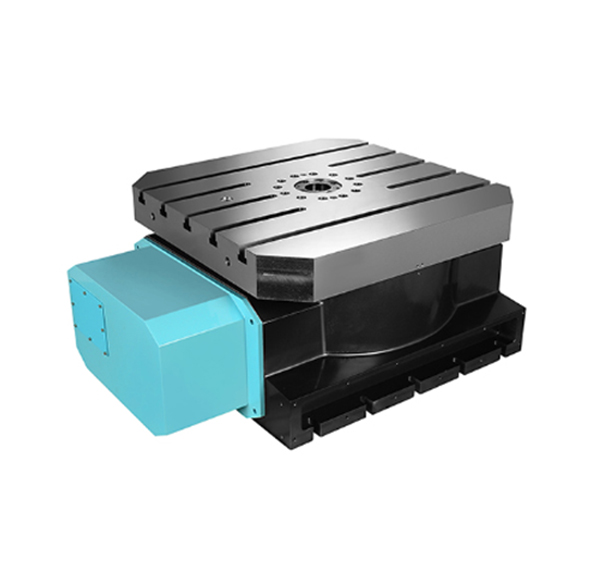

Practical Applications
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, four – axis rotary tables are used in the manufacturing of engine components. The precise movement and rotation capabilities are essential for machining turbine blades. The ability to rotate the workpiece around the A – axis allows for the creation of the complex airfoil shapes required for optimal engine performance.
Automotive Manufacturing
When manufacturing engine blocks or transmission parts, the four – axis rotary table is used to perform multiple machining operations in a single setup. The X, Y, and Z axes can position the tool for drilling, milling, and boring operations, while the A – axis can rotate the part to machine different faces without the need for re – clamping, which improves accuracy and reduces production time.
Medical Device Production
For manufacturing surgical instruments or implants, the four – axis rotary table is used to create intricate geometries. The precise control of all four axes ensures that the parts meet the strict tolerances required in the medical field. For example, in the production of hip implants, the A – axis rotation is used to shape the curved surfaces of the implant accurately.
In conclusion, the four – axis rotary table’s working principle, with its four axes of movement, enables a wide range of applications in different industries. Its ability to precisely position and rotate workpieces is invaluable for creating complex and high – quality products.











